The Ultimate Guide to QSFP Cables: What You Need to Know?
Choosing the right high-speed interconnect is a critical step in any data center or telecom deployment. One of the most versatile and future-ready options available today is the Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable (QSFP) cable. Whether you are upgrading to 100G, deploying 400G, or planning ahead for next-gen connectivity, understanding QSFP cables will help you make the right investment.
In this ultimate guide, I’ll break down exactly what QSFP cables are, how they compare to SFP and SFP+, how to choose the right type, installation and maintenance best practices, and the real benefits you can expect.
What is a QSFP Cable?
QSFP cables are high-speed transceiver and cabling solutions that combine four lanes of data transmission in one compact form factor. Originally designed for 40G Ethernet (QSFP+), they have evolved to support 100G, 200G, and 400G speeds with new standards like QSFP28 and QSFP-DD.
Unlike a simple copper patch cord, a QSFP cable can be:
- An active optical cable (AOC) with built-in transceivers at each end.
- A direct attach copper cable (DAC) for short-range, low-cost connections.
- A breakout cable (e.g., QSFP28 to 4× SFP28) to connect multiple devices at lower speeds.
For a technical overview, you can refer to Cisco’s official QSFP transceiver module datasheet1 which covers QSFP, QSFP+, QSFP28, and newer QSFP-DD models.

Common QSFP Standards
| QSFP Type | Data Rate | Typical Use Case | Max Distance | Medium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QSFP+ | 40G | Aggregation, short DCI | 100–150 m (MMF) | Fiber / Copper |
| QSFP28 | 100G | Spine-leaf, metro DCI | 10–40 km (SMF) | Fiber |
| QSFP56 | 200G | HPC, AI workloads | 100 m – 10 km | Fiber |
| QSFP-DD | 400G | Cloud & hyperscale | 500 m – 10 km | Fiber |
For IEEE specifications, see the IEEE 802.3 Ethernet standard2 for each physical layer definition.
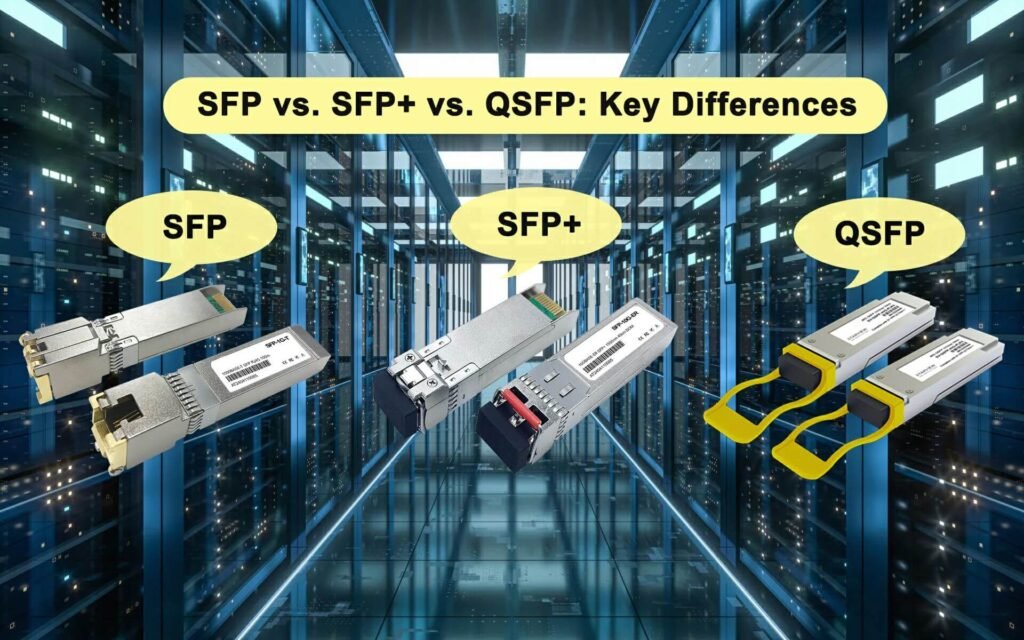
SFP vs SFP+ vs QSFP: What’s the Difference?
If you’re confused between SFP, SFP+, and QSFP, you’re not alone. They look similar but serve different purposes.
Quick breakdown:
- SFP: Small Form-factor Pluggable, supports up to 1G.
- SFP+: Enhanced SFP, supports up to 10G.
- QSFP: Quad version, supports four channels — 4×10G (40G) or 4×25G (100G).
For example, a QSFP-100G-LR4-S transceiver uses four 25G lanes multiplexed over single-mode fiber to achieve 100G line rate, as explained in Cisco’s QSFP-100G-LR4-S product page3.
Side-by-Side Comparison
| Feature | SFP | SFP+ | QSFP28 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Speed | 1G | 10G | 100G |
| Lane Count | 1×1G | 1×10G | 4×25G |
| Typical Use | Access | Access / Aggregation | Core / Spine |
| Connector | LC duplex | LC duplex | LC duplex / MPO |
Why it matters:
If you are planning a spine-leaf upgrade to 100G or higher, QSFP is the right choice due to density, bandwidth, and scalability.
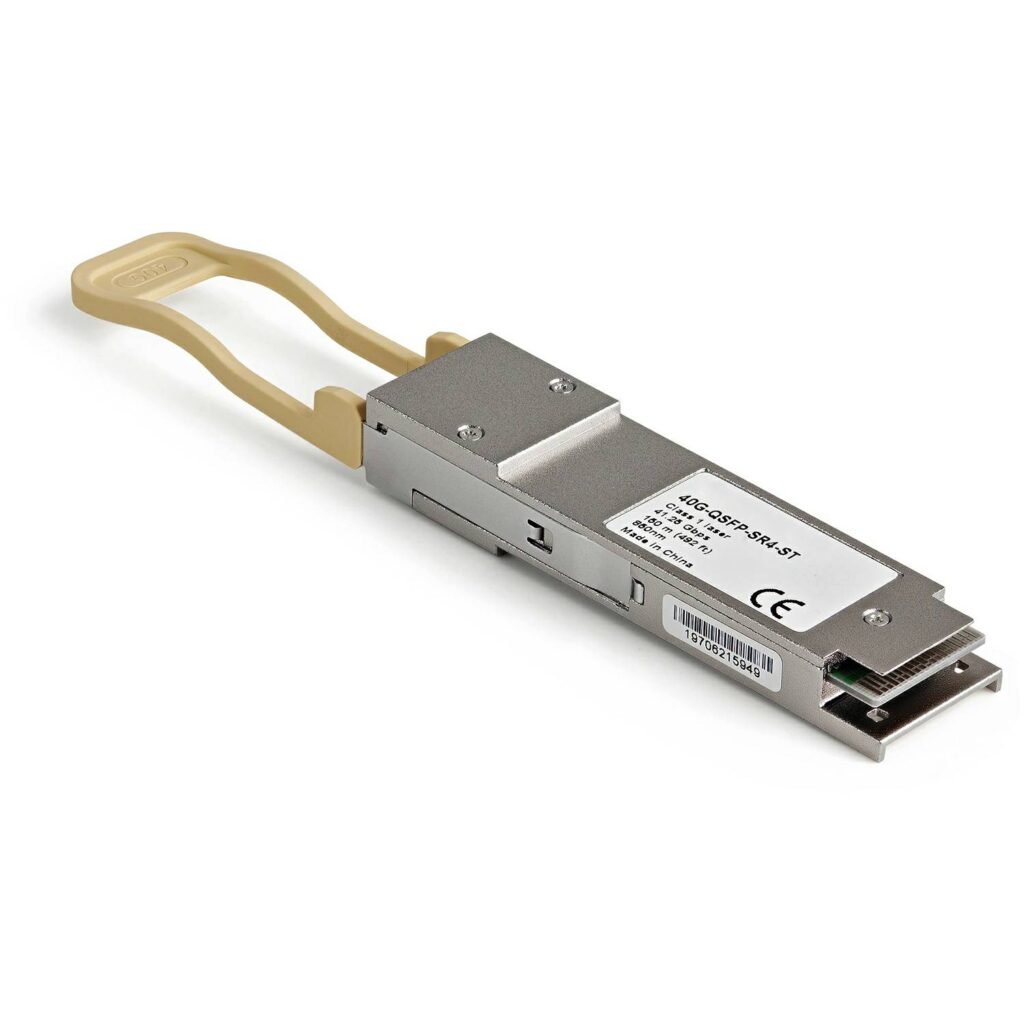

How to Choose the Right QSFP Cable?
Choosing a QSFP cable isn’t just about matching the speed. You need to consider:
- Speed and Standard: QSFP+ (40G), QSFP28 (100G), QSFP-DD (400G).
- Reach: Do you need short-reach DAC/AOC or long-reach LR4/ZR modules?
- Connector Type: LC duplex for single-mode, MPO/MTP for parallel optics.
- Compatibility: Check switch firmware for whitelist support.
- Power Consumption: Important in dense racks for cooling.
- Budget: Balance between OEM and third-party modules.
For a detailed guide on choosing the right module, FS.com’s QSFP transceiver selection guide4 is an excellent reference.
Example Decision Table
| Requirement | Recommended QSFP Solution |
|---|---|
| ≤ 5 m in-rack | Passive QSFP DAC |
| ≤ 100 m intra-data center | QSFP AOC |
| ≤ 10 km metro | QSFP-100G-LR4-S |
| ≤ 40 km long-haul | QSFP-100G-ER4 |
How to Install and Maintain QSFP Cables?
Installation and maintenance directly affect QSFP cable lifespan and performance.
Installation best practices:
- Always leave dust caps on until ready to mate.
- Clean connectors with an optical cleaning kit5 before insertion.
- Avoid excessive bending — follow the cable’s minimum bend radius.
- Verify link performance with an optical power meter.
Maintenance tips:
- Schedule periodic inspections.
- Keep an eye on Digital Optical Monitoring (DOM) values via your network OS.
- Store spares in anti-static bags in a temperature-controlled environment.
Cisco offers a detailed transceiver installation guide6 that covers handling, cleaning, and ESD safety.
What Are the Benefits of Using QSFP Cables?
The benefits of QSFP cables extend beyond speed:
- High density: Four lanes in one module reduce the number of ports required.
- Scalability: Upgrade from 40G to 100G or 400G without replacing chassis.
- Lower power per Gbps: Efficient design reduces cooling costs.
- Flexibility: Support for Ethernet, InfiniBand, and Fibre Channel.
- Interoperability: Compliant with IEEE and MSA standards.
IEEE’s Optical Module Standards overview7 explains how QSFP modules comply with Ethernet PHY specifications.
Conclusion
QSFP cables are a cornerstone of modern high-speed networks, offering scalability, performance, and flexibility for a wide range of applications — from short-reach in-rack connections to long-distance metro links.
By understanding the differences between QSFP models, installation best practices, and compatibility requirements, you can deploy a future-ready network that meets both current and future demands.
If you’re sourcing QSFP-100G-LR4-S or other QSFP cable assemblies, you can explore solutions from Abptel8 or cross-check specifications with Cisco and FS.com before making a purchase.
-
Cisco — Transceiver Modules – Data Sheets ↩
-
Cisco — QSFP-100G-LR4-S Data Sheet ↩
-
FS.com — QSFP Transceiver Selection Guide ↩
-
FS.com — Fiber Optic Cleaning Tools ↩
-
Cisco — Transceiver Installation Guide ↩