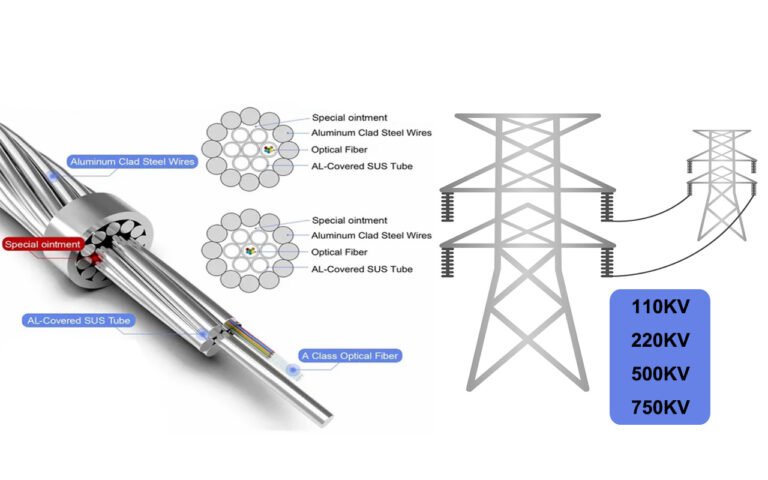
OPGW vs Traditional Ground Wire: What Are the Pros and Cons?
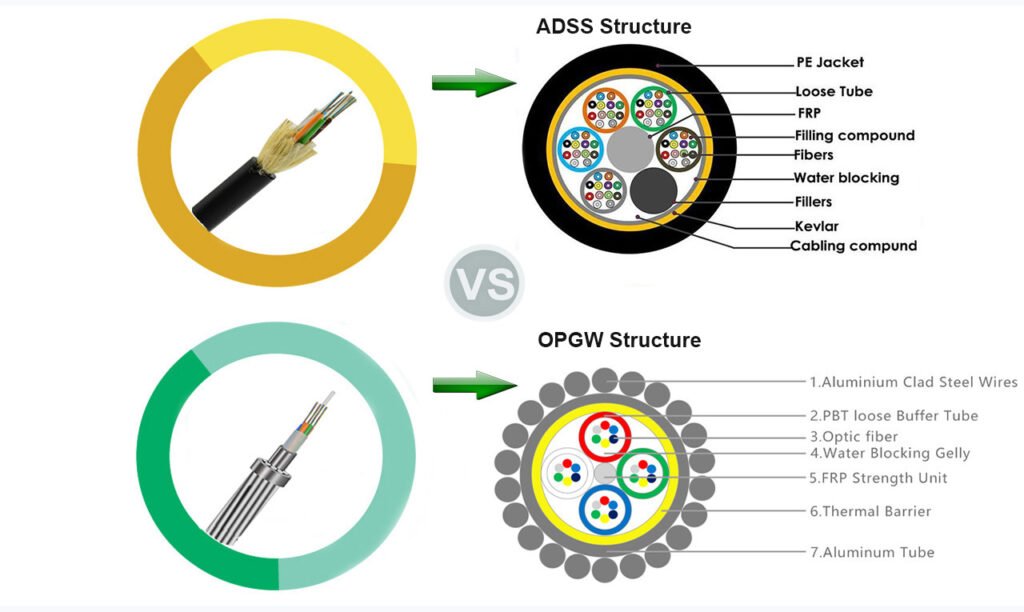
In the realm of power transmission, choosing the right ground wire is crucial. However, the decision between Optical Ground Wire (OPGW)1 and traditional ground wires can be daunting due to their distinct functionalities and attributes.
OPGW offers dual functionality, combining electrical grounding with communication capabilities, providing advanced features like high-speed data transmission and improved reliability. Traditional ground wires, however, are simpler and cheaper to install but lack integrated communication features and adaptability.
Imagine the power grid as a bustling highway system; every component must perform reliably to ensure smooth traffic flow. Engineers and managers must weigh the pros and cons of OPGW and traditional wires to optimize performance, cost, and future scalability in their infrastructure projects.
How Does OPGW Compare to Traditional Ground Wire?
The choice between OPGW and traditional ground wires hinges on various factors including their functionality2, installation complexity3, and cost implications. Understanding these differences is essential for making an informed decision.
OPGW provides dual functionality, enhancing communication capabilities alongside grounding. Traditional wires focus solely on grounding, leading to simpler installations but requiring additional infrastructure for communication.
When evaluating OPGW, its dual functionality stands out. Not only does it serve as a ground wire, but it also integrates high-speed communication, essential for modern power systems that demand real-time data transmission and monitoring. This dual role can significantly streamline infrastructure, reduce costs, and future-proof the grid against technological advancements4.
Pros of OPGW
Dual Functionality
- OPGW integrates electrical protection with communication, merging grounding and data transmission roles. This dual function simplifies infrastructure by eliminating the need for separate communication lines, thereby reducing both installation and maintenance expenses.
Enhanced Communication
- The optical fibers within OPGW5 facilitate high-speed data transmission, crucial for real-time monitoring and remote control. This capability ensures that power transmission lines are not only protected but also smartly managed.
Anti-Electromagnetic Interference
- OPGW’s optical fibers are immune to electromagnetic interference6, guaranteeing stable communication even in high-voltage environments. This resistance ensures reliable data transmission, which is vital for maintaining system integrity.
High Temperature Resistance
- OPGW can withstand extreme temperatures7, ensuring functionality in harsh environments where traditional wires might falter. This resilience makes it ideal for regions with challenging climate conditions.
Cost Efficiency
- By combining grounding and communication in one cable, OPGW reduces the need for additional infrastructure, translating into cost savings during both installation and upkeep.
Improved Reliability
- OPGW enhances system reliability by offering robust protection against electrical disturbances and lightning strikes, crucial for maintaining consistent power transmission.
Future Proofing
- The optical fibers within OPGW support evolving communication needs, making the power grid adaptable to future technological advancements8.
Cons of OPGW
Complex Installation
- Installing OPGW requires meticulous integration into existing infrastructure, increasing installation costs9 and time due to its complexity.
Electrical Hazards
- Metallic components in OPGW raise electrical hazard risks10, necessitating careful handling to prevent short circuits and arcing during installation and maintenance.
Maintenance Requirements
- Regular inspections are vital to prevent corrosion or degradation of OPGW’s metallic parts, ensuring sustained performance over time.
Weight and Tension
- The additional weight from OPGW’s metal components can increase tension on support structures, requiring precise engineering to maintain stability.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Ground Wires?
Traditional ground wires have been a staple in power transmission systems due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. However, they come with limitations in functionality and adaptability.
Traditional ground wires are easier and cheaper to install than OPGW cables, yet they lack the high-speed communication capabilities and advanced features that modern power systems demand.
Pros of Traditional Ground Wires
Simpler Installation
- Traditional ground wires are straightforward to install as they do not involve complex integration of optical fibers, reducing installation time and effort.
Lower Initial Cost
- Without the need for additional materials like optical fibers, traditional wires have lower upfront costs, making them an economical choice for basic grounding needs.
Established Technology
- With well-understood installation and maintenance protocols, traditional wires offer reliability through proven technology11.
Cons of Traditional Ground Wires
Single Functionality
- Serving solely as grounding elements, traditional wires lack the communication capabilities inherent in OPGW, necessitating separate systems for data transmission.
Lack of Advanced Features
- Traditional wires do not provide high-speed data transmission, real-time monitoring, or resistance to electromagnetic interference, limiting their utility in modern grids.
Limited Adaptability
- As power systems evolve, traditional wires struggle to meet new demands, lacking the flexibility and integrated functionality of their OPGW counterparts.
Conclusion
In summary, selecting between OPGW and traditional ground wires involves balancing functionality, cost, and future needs. OPGW offers a sophisticated solution with dual functionality, high-speed communication, and adaptability, albeit with higher installation complexity and cost. Traditional ground wires, while simpler and cheaper initially, fall short in terms of communication capabilities and future-proofing.
Ultimately, the choice depends on the specific requirements of the power infrastructure and the long-term vision for grid development. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each option enables engineers and managers to make informed decisions, ensuring both immediate and future needs are met efficiently.
-
Provides a basic understanding of what OPGW is and its applications in the industry. ↩
-
Highlights the functional differences between OPGW and traditional ground wires, offering a detailed comparison. ↩
-
Elaborates on the technical challenges involved in installing OPGW, offering insights into costs and methodology. ↩
-
Discusses the evolving technologies in power systems that OPGW supports, reinforcing its benefit of future proofing. ↩
-
Provides in-depth information on how optical fibers function within OPGW, enhancing data transmission capabilities. ↩
-
Explains electromagnetic interference and how OPGW’s immunity contributes to system reliability. ↩
-
Describes OPGW’s ability to withstand extreme temperatures which is essential for use in harsh environmental conditions. ↩
-
Describes how OPGW is adaptable to future changes and technologies, offering longevity in grid systems. ↩
-
Details the cost factors for OPGW installation, aiding in budget assessments and project planning. ↩
-
Provides safety information regarding potential electrical hazards from OPGW, important for installation precautions. ↩
-
Justifies the reliability of traditional ground wires based on long-term use and established technology. ↩