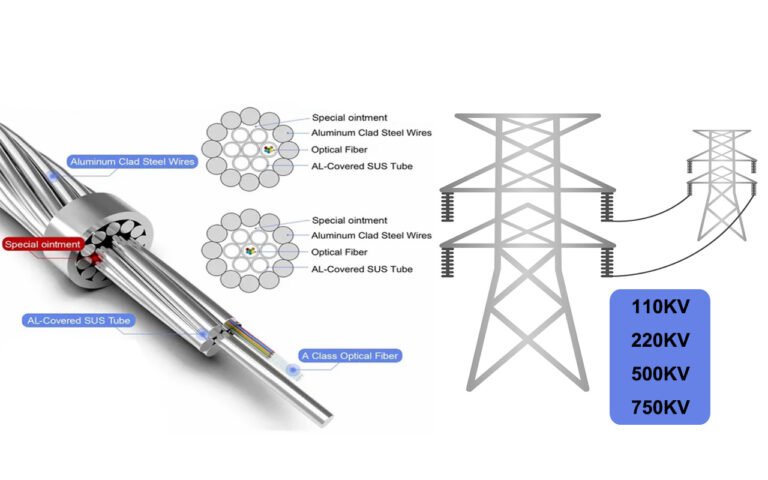
What Are the Key Differences Between OPGW and ADSS Cables?
In the complex realm of fiber optics, choosing the right cable type is crucial. Misunderstanding your options can lead to costly errors. But fear not; I explore the differences between Optical Ground Wire (OPGW)1 and All-Dielectric Self-Supporting (ADSS)2 cables to aid your decision-making.
**OPGW cables combine optical fibers with metallic components for dual functionality in communication and grounding, mainly used in high-voltage power lines. Conversely, ADSS cables are all-dielectric, ideal for telecommunications and resistant to electromagnetic interference3, making them suitable for high-voltage environments.
Transition paragraph: Understanding the right choice between OPGW and ADSS cables involves exploring their design, applications, installation costs, and environmental resistance. Each cable type offers distinct advantages that cater to different industrial needs. Let me delve deeper into what makes each unique and their specific applications.
How Do Structure and Composition Differ in OPGW and ADSS Cables?
The structural differences between OPGW and ADSS cables are significant. These differences influence their applications and performance in various environments, particularly in how they handle electromagnetic interference and mechanical stress.
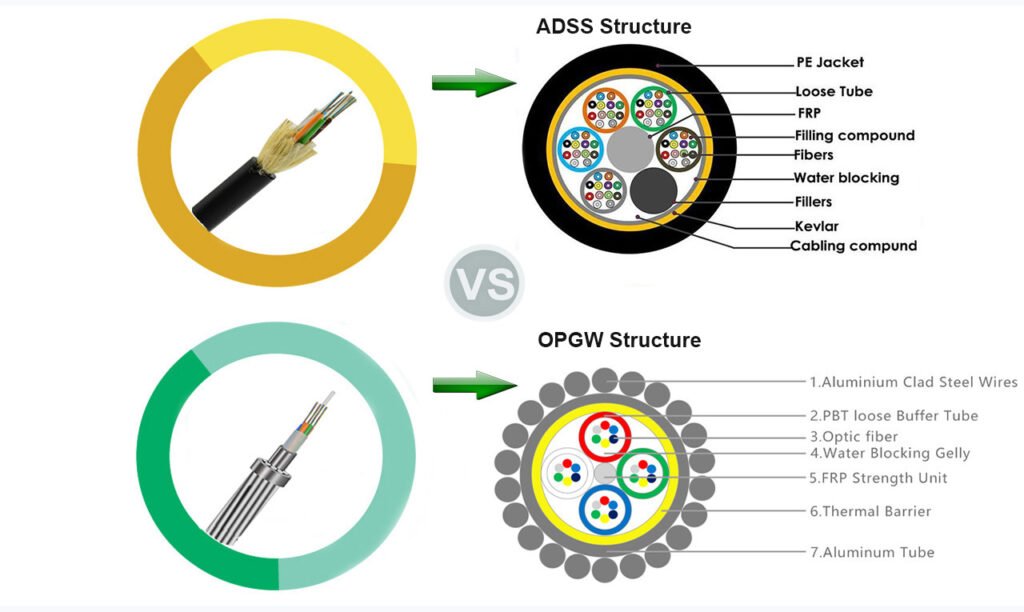
OPGW cables have a metallic core for mechanical strength4 and electrical conductivity5, combining optical fibers with metal. ADSS cables are entirely non-metallic, relying on aramid yarns for support, which makes them immune to electromagnetic interference.
Structure of OPGW Cables
OPGW cables are constructed with a metallic core surrounded by protective layers, often stainless steel or aluminum-clad steel tubes. This design ensures durability and functionality in high-stress environments. The table below outlines the typical composition:
| Component | Material Used | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Core | Steel/Aluminum-clad | Provides mechanical strength and electrical path |
| Optical Fibers | Glass | Facilitates data transmission |
| Protective Layers | Stainless Steel Tubes | Shields the fibers from environmental damage |
I recall a project where we had to install OPGW cables across a region prone to lightning strikes. The metallic core not only provided the necessary grounding but also ensured that the optical fibers remained intact and operational, despite the harsh environmental conditions. This dual functionality was a game-changer, significantly reducing both maintenance costs and downtime.
Composition of ADSS Cables
ADSS cables eschew metal entirely, using aramid yarns6 or glass-reinforced plastic rods for support. This makes them a perfect fit for areas with high electromagnetic interference. Their design is simpler and often more cost-effective.
| Component | Material Used | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Support Material | Aramid Yarns/GRP Rods | Provides mechanical strength |
| Optical Fibers | Glass | Facilitates data transmission |
| Outer Coating | UV-Resistant Polymer | Protects against environmental elements |
In one installation I oversaw in an urban area with heavy electrical traffic, ADSS cables were the go-to choice. Their all-dielectric construction ensured that electromagnetic interference from nearby power lines did not disrupt the data transmission capabilities of the network. Additionally, their lightweight nature made the installation process smoother and faster, reducing labor costs and project timelines.
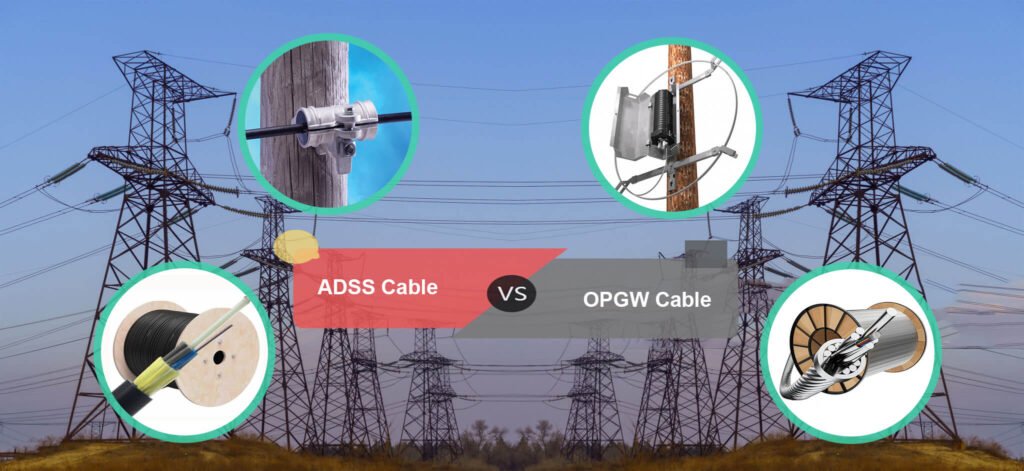
What Applications Suit OPGW and ADSS Cables Best?
Choosing between OPGW and ADSS cables often depends on their intended applications. They serve different roles in power transmission and telecommunications, influenced by their design and material composition.
OPGW cables are best suited for high-voltage power lines, serving as both grounding and communication mediums. ADSS cables excel in telecommunication networks, especially where electromagnetic interference is a concern.
Understanding where each cable type shines can help you make informed decisions that enhance both performance and reliability.
Applications of OPGW Cables
- High-Voltage Lines: Used for grounding and communication, protecting against lightning.
- Power System Safety: Enhances system stability and reduces fault risk.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Facilitates continuous monitoring of power grid operations.
- Data Transmission: Supports high-speed data communication for utility management.
I remember working on a high-voltage transmission project where the integration of OPGW cables was pivotal. Not only did they provide the necessary grounding to protect against electrical faults, but they also served as a robust medium for data transmission, enabling real-time monitoring and control of the power grid. This dual functionality eliminated the need for separate communication lines, reducing overall infrastructure costs and simplifying maintenance procedures.
Applications of ADSS Cables
- Telecommunication Networks: Perfect for long and short-distance data transmission.
- High-EMI Environments: Non-metallic nature prevents interference from nearby power lines.
- Railway Communication Systems: Provides reliable data transmission in environments with significant electromagnetic noise.
- Urban Fiber Deployments: Ideal for densely populated areas where electromagnetic interference is prevalent.
In another project involving the expansion of a city’s fiber network, ADSS cables were chosen for their resistance to electromagnetic interference. Their all-dielectric nature ensured that the high-speed data transmission remained unaffected by the city’s bustling electrical infrastructure. Moreover, their ability to be installed on existing poles without additional support structures made the deployment process efficient and cost-effective.
How Do Installation and Cost Compare Between OPGW and ADSS Cables?
Installation complexity and cost are critical factors when choosing between OPGW and ADSS cables. These factors can influence project timelines and budgets significantly.
OPGW cables require more complex and costly installation processes7 due to grounding needs. In contrast, ADSS cables are easier and more cost-effective to install, often utilizing existing infrastructure.
From my experience, the decision between these two cable types often comes down to balancing the initial installation costs against the long-term benefits they provide.
Installation of OPGW Cables
- Complex Process: Requires precise grounding and coordination.
- Higher Costs: Due to specialized installation needs and equipment.
- Specialized Training: Installation teams need to be well-versed in handling both electrical and communication components.
- Safety Measures: Additional safety protocols are necessary to handle high-voltage environments.
Installing OPGW cables is no small feat. The process involves ensuring that the metallic core is properly grounded, which necessitates specialized equipment and meticulous execution. During a project in a remote area, the installation team faced challenges related to difficult terrain and the need for precise tensioning. However, the investment paid off as the cables provided both effective grounding and reliable data transmission capabilities. This dual functionality not only enhanced the system’s reliability but also reduced the need for additional infrastructure, leading to long-term cost savings.
Installation of ADSS Cables
- Ease of Installation: Can be installed on existing structures.
- Cost-Effective: Lower overall costs and faster deployment.
- Flexibility: Suitable for various terrains and urban environments.
- Minimal Safety Concerns: Being all-dielectric, they pose fewer electrical hazards.
On the flip side, ADSS cables offer a more straightforward installation process. They can be easily strung along existing poles and towers without the need for additional grounding infrastructure. In a recent urban telecommunication project, the use of ADSS cables allowed for a rapid deployment schedule, reducing both labor costs and project timelines. Their lightweight and flexible nature made them ideal for installations in areas with limited access and complex infrastructure, ensuring that the project stayed on budget and was completed on time.
What About Environmental and Mechanical Resistance?
Environmental resilience and mechanical strength are crucial for cable longevity. OPGW and ADSS cables each offer distinct advantages in these areas, largely due to their material composition.
OPGW cables provide robust mechanical support and resistance to environmental hazards due to their metallic components. ADSS cables offer excellent resistance to environmental factors like UV rays and EMI thanks to their non-metallic construction.
Each cable type is engineered to withstand the specific challenges posed by their installation environments, ensuring long-term reliability and performance.
Environmental Resistance of OPGW Cables
- Mechanical Strength: Withstands physical stress and harsh environments.
- Electrical Protection: Designed to handle electrical surges and faults.
- Weather Resistance: Resists damage from lightning, wind, and ice.
- Durable Coatings: Protects against corrosion and environmental degradation.
OPGW cables are built to endure the rigors of high-voltage environments. Their metallic cores not only provide mechanical strength but also offer protection against electrical surges, such as lightning strikes. During a severe storm in North America, the OPGW cables I worked with demonstrated exceptional resilience, maintaining both grounding and communication functionalities despite the extreme weather conditions. Their ability to resist corrosion and withstand physical stress ensures that they remain operational and reliable over long periods, even in the most challenging environments.
Environmental Resistance of ADSS Cables
- UV and Temperature Resistance: Withstands harsh environmental conditions.
- EMI Immunity: Perfect for high-interference areas.
- Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: Protects against water ingress and corrosion.
- Flexible Materials: Adapts to varying environmental stresses without degrading.
ADSS cables excel in environments where electromagnetic interference is prevalent. Their all-dielectric design makes them immune to interference from nearby electrical systems, ensuring uninterrupted data transmission. Additionally, their UV-resistant coatings protect against sun degradation, while their construction materials withstand extreme temperatures and moisture levels. This makes ADSS cables ideal for installation in areas with fluctuating weather patterns and high electromagnetic activity. For instance, in a coastal project where salt spray and high humidity were concerns, ADSS cables performed exceptionally well, maintaining their integrity and functionality without any signs of corrosion or degradation.
What Are the Key Differences Between OPGW and ADSS Cables?
Understanding the key differences between OPGW and ADSS cables is essential for making informed decisions in fiber optic network deployments. These differences span various aspects, including structure, composition, applications, installation processes, and environmental resistance.
The primary distinctions between OPGW and ADSS cables lie in their structural design, material composition, and intended applications. OPGW cables integrate metallic components for dual functionality, while ADSS cables are entirely non-metallic, offering specific advantages in certain environments.
Delving deeper into these differences can provide valuable insights into selecting the most suitable cable type for your project’s unique requirements.
Structure and Composition
As previously discussed, OPGW cables combine metallic cores with optical fibers, providing both mechanical strength and electrical conductivity. This hybrid design allows them to serve as both grounding systems and communication mediums. In contrast, ADSS cables rely on aramid yarns or glass-reinforced plastic rods for support, eliminating the need for metallic components and enhancing their immunity to electromagnetic interference.
Applications and Use Cases
OPGW cables are predominantly used in high-voltage power transmission lines, where their dual functionality is indispensable. They not only protect against electrical faults and lightning strikes but also facilitate high-speed data transmission for monitoring and control systems. On the other hand, ADSS cables are favored in telecommunications networks, especially in environments where electromagnetic interference is a concern. Their all-dielectric nature makes them ideal for installations near power lines, railway systems, and urban infrastructure.
Installation Processes and Costs
The installation of OPGW cables is inherently more complex and costly due to the need for precise grounding and specialized equipment. This complexity is balanced by the long-term benefits of having integrated grounding and communication functionalities. ADSS cables, being easier and more cost-effective to install, offer flexibility and quicker deployment times, making them suitable for projects with tighter budgets and shorter timelines.
Environmental and Mechanical Resistance
While both cable types offer robust environmental resistance, their approaches differ. OPGW cables rely on their metallic cores to provide mechanical strength and electrical protection, making them resilient against physical stresses and electrical surges. ADSS cables, with their all-dielectric construction, excel in environments with high electromagnetic interference and offer superior resistance to UV rays and moisture, ensuring longevity and consistent performance.
Conclusion
Choosing between OPGW and ADSS cables hinges on the specific needs of a project. OPGW cables are ideal for high-voltage power systems, where grounding and communication are necessary. They offer robust mechanical strength and dual functionality, albeit at a higher installation cost. ADSS cables, however, are better suited for telecommunications, especially in high-EMI environments, where their non-metallic nature offers significant advantages. They are cost-effective, easy to install, and resistant to environmental conditions. Understanding these differences ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency for your fiber optic network needs.
Overall, OPGW cables are not just a technical innovation; they are a strategic asset in the pursuit of a more connected and resilient infrastructure. My journey with ABPTEL has reinforced the importance of such technologies, and I am excited to see how OPGW and ADSS cables will continue to shape the industries they serve. Whether enhancing power grid stability or ensuring seamless data transmission in telecommunications networks, both cable types play pivotal roles in modern infrastructure development.
By carefully assessing the unique requirements of your projects and understanding the strengths of each cable type, you can make informed decisions that drive efficiency, reliability, and long-term success. Embracing the right fiber optic technologies not only optimizes operational performance but also positions your organization at the forefront of innovation in the ever-evolving telecommunications landscape.
Footnotes
-
The term Optical Ground Wire (OPGW) refers to a type of cable used in telecommunications to protect power lines and provide data transmission. It’s crucial for readers to understand its dual function in infrastructure projects. ↩
-
All-Dielectric Self-Supporting (ADSS) cables are a type of fiber optic cable that does not contain any metallic components, making them immune to electromagnetic interference and suitable for use near high-voltage power lines. ↩
-
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) refers to disturbances that affect electrical circuits due to electromagnetic radiation emitted from external sources. Understanding EMI is essential for choosing the right type of cable to ensure data integrity. ↩
-
Mechanical strength in cables refers to their ability to withstand physical stresses such as tension, wind, and weight without breaking or deforming. This is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the cable in various installation environments. ↩
-
Electrical conductivity in cable materials determines how well a cable can carry electrical current. In OPGW cables, high conductivity is essential for their role in grounding and protecting power lines from electrical faults. ↩
-
Aramid yarns, such as Kevlar, are strong, lightweight fibers used in ADSS cables to provide structural support without adding electrical conductivity, thereby preventing electromagnetic interference. ↩
-
The installation process for OPGW and ADSS cables varies in complexity and cost. OPGW installation is typically more involved due to the need for grounding and specialized equipment, while ADSS installation is generally simpler and more cost-effective, leveraging existing infrastructure. ↩