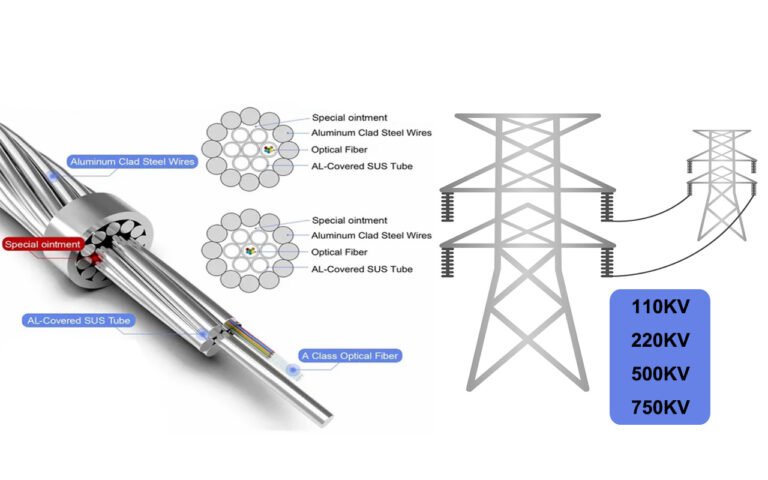
How Do You Properly Terminate OPGW Cables?
In the telecommunications world, improperly terminated Optical Ground Wire (OPGW)1 cables can lead to severe network issues. Imagine the chaos of signal loss or network downtime due to a faulty connection. The solution? Mastering the art of OPGW cable termination2 ensures seamless communication and robust connections.
Proper termination of OPGW cables involves precise steps like careful handling3, removing outer layers, cleaning fibers, and securing with clamps. These steps maintain cable integrity and functionality, ensuring efficient and reliable network performance.
Picture a busy telecom engineer racing against time to restore network connectivity. The pressure is immense, but with the right knowledge of OPGW cable termination, they can swiftly bring everything back online. This guide will walk you through every critical step, ensuring your network isn’t left hanging.
What Are the Steps for Preparing and Handling OPGW Cables?
Before you even think about termination, preparation is key. Handling OPGW cables with care is crucial to prevent damage that can compromise performance. Start by ensuring the cable is straightened over at least 2.5 meters4 to avoid twists or kinks.
Straightening OPGW cables to a minimum of 2.5 meters ensures there are no kinks or twists, which is crucial for maintaining cable integrity during termination.
Straightening the cable might seem simple, but it is a critical step. Twists or kinks can cause microbending5, leading to signal loss. Mark the cable at the desired length, securing it with tape to ensure precise cutting. This step prevents unnecessary wastage and ensures accurate termination.
How Do You Remove Outer Layers and Prepare the Fibers?
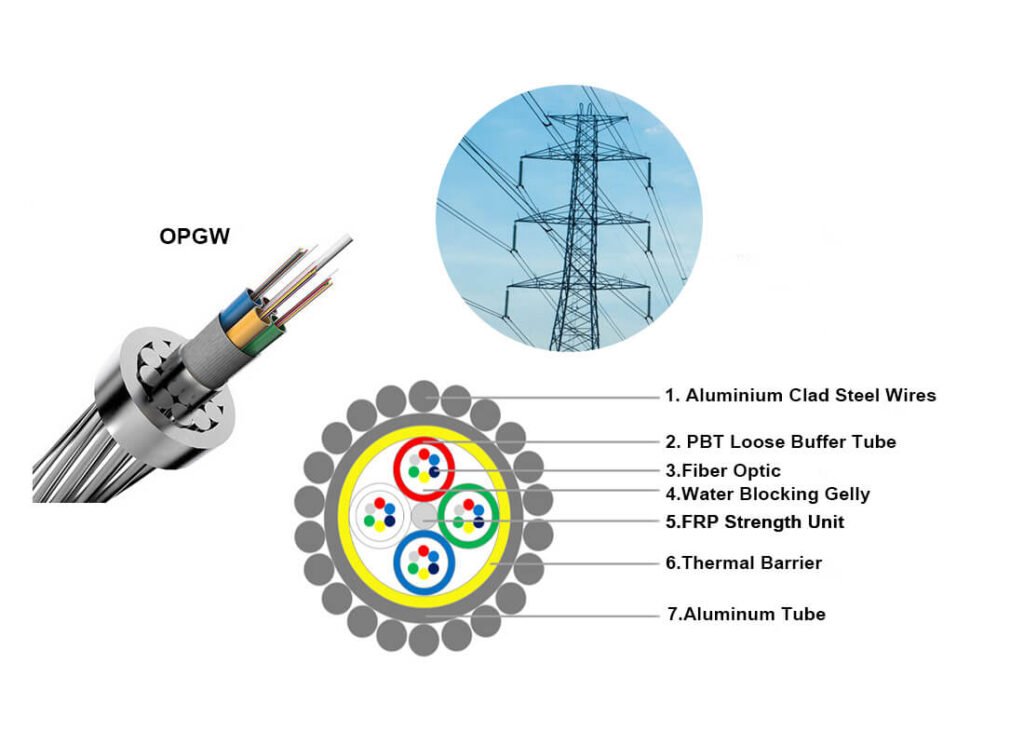
Once your cable is prepared, the next step involves removing outer layers to access the delicate fibers within. This requires precision and care to avoid damaging the fibers, which are essential for signal transmission6.
Removing the aluminum strands and outer layers of the OPGW cable exposes the fiber optic cores7, which is essential for proper termination.
Use a file to smooth any sharp edges after removing the aluminum strands8. Carefully separate the metal loose tubes without damaging them. Specialized tools like strippers and cleavers9 are essential for stripping jackets and coatings, revealing the fiber cores. This precision ensures optimal signal transmission.
Why Is Cleaning the Fibers Crucial?
With the fibers exposed, cleanliness becomes paramount. Any dust or contaminants can lead to signal loss, making fiber cleaning10 a non-negotiable step.
Cleaning OPGW fibers with alcohol wipes removes contaminants, ensuring a reliable and efficient signal transmission.
Contaminants on fibers can cause signal attenuation11. Clean each fiber meticulously with alcohol wipes to remove dust or debris. This step ensures a clean, direct path for the light signal, maximizing the efficiency of your network.
What Are the Best Practices for Installing Cable Clamps and Sealing?
After cleaning, securing the fibers with cable clamps and proper sealing is crucial to protect them from environmental factors like moisture.
Use heat-shrinkable sleeves12 and cable clamp cylinders to secure and seal OPGW fibers, protecting them from moisture and damage.
Proper alignment and securing of cable clamp cylinders over metal loose tubes is vital. Heat-shrinkable sleeves seal the tubes, preventing moisture ingress. In cases of multiple loose tubes, built-up tubes and hot air guns are used to secure and seal the cables effectively.
How Do You Secure the Cable to Structures?
Securing the OPGW cable to poles or towers requires careful tensioning to prevent stress or damage, ensuring long-term reliability.
Tension clamps13 maintain the minimum bending radius, securing OPGW cables without causing stress or torsion during installation.
Maintain the minimum allowed bending radius14 to avoid microbending. Use tension clamps and wrap the cable around tension machines to prevent torsion. Properly prepare the traction end to avoid extra torsion during the pay-off period, ensuring stable and secure installation.
Why Is Electrical Bonding Important?
Electrical bonding15 is a critical step, ensuring the OPGW cable is integrated into the electrical grounding system for safety and functionality.
Bond OPGW cables electrically with supporting structures using pre-assembled earth bonding leads16 with compression terminals.
Proper electrical bonding prevents electrical faults and enhances safety. Use pre-assembled earth bonding leads, ensuring secure connections with compression terminals. This integration is vital for protecting both the cable and the structure from electrical damage.
What Are the Final Adjustments and Testing Procedures?
Once all components are secured, final adjustments and thorough testing confirm the integrity and performance of the termination.
Adjust cable sag, install downlead clamps, and perform integrity tests17 to ensure proper OPGW cable termination.
Tighten cable sag using tools like spanner bottles18 to meet design specifications. Install downlead clamps and ensure all connections are clean. Conduct tests to verify the termination’s effectiveness, ensuring optimal network performance.
Conclusion
Terminating OPGW cables is a meticulous process that demands attention to detail at every stage. From careful preparation and handling to precise removal of outer layers, cleaning, securing, and electrical bonding, each step ensures the cable’s integrity and performance. By following these guidelines, telecom engineers and product managers can achieve reliable and efficient network connections. Remember, a well-terminated OPGW cable is the backbone of seamless communication and robust network infrastructure.
-
OPGW cables are used in power utility infrastructure to combine grounding and fiber-optic communication functions. ↩
-
OPGW cable termination involves a series of precise steps to ensure the integrity of the connection, including proper handling, fiber cleaning, and securing with clamps. ↩
-
Careful handling of OPGW cables is essential to avoid damaging the fibers, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. ↩
-
Straightening OPGW cables to at least 2.5 meters prevents twists or kinks, which can compromise the signal integrity during termination. ↩
-
Twists or kinks can cause microbending, a phenomenon that leads to signal loss in fiber optic cables. ↩
-
Signal transmission in fiber optics relies on the proper handling and preparation of cables, ensuring that light signals pass through without loss or distortion. ↩
-
Fiber optic cores are the central components that carry the light signals, and they must be properly exposed during the termination process. ↩
-
Aluminum strands serve as an essential component in OPGW cables, providing mechanical strength and electrical grounding. ↩
-
Strippers and cleavers are specialized tools used to strip jackets and cleave fibers, ensuring precision when preparing the fibers for connection. ↩
-
Fiber cleaning methods, such as using alcohol wipes, ensure that the fibers are free of contaminants that could interfere with signal transmission. ↩
-
Signal attenuation refers to the reduction in signal strength as it travels through the fiber, and cleaning fibers helps to minimize this loss. ↩
-
Heat-shrinkable sleeves are used to protect OPGW fibers from environmental factors like moisture, ensuring that the connections remain intact. ↩
-
Tension clamps maintain the minimum bending radius and prevent stress or torsion during installation, ensuring the OPGW cables remain undamaged. ↩
-
The bending radius refers to the smallest curve a fiber optic cable can make without affecting performance. Maintaining the correct radius is crucial to prevent microbending. ↩
-
Electrical bonding integrates the OPGW cable into the grounding system of the electrical network, ensuring safety and proper functionality. ↩
-
Earth bonding leads with compression terminals are used to securely bond OPGW cables to supporting structures, preventing electrical faults. ↩
-
Integrity tests verify that the OPGW cable has been properly terminated and that the connections are functional and reliable. ↩
-
Spanner bottles are used to adjust cable sag to meet design specifications, ensuring proper tension during installation and optimal performance. ↩